Intro
If you’ve been keeping up with my earlier blog entries, such as 01-caddy-in-docker and 06-caddy-for-quartz, you now have on your server a Caddy Docker instance successfully serving a static site powered by Quartz.
Given that I edit my notes using multiple devices, Obsidian and Obsidian Git plugin, I’ve been searching for a solution for automatically deploying my Quartz changes directly to my server.
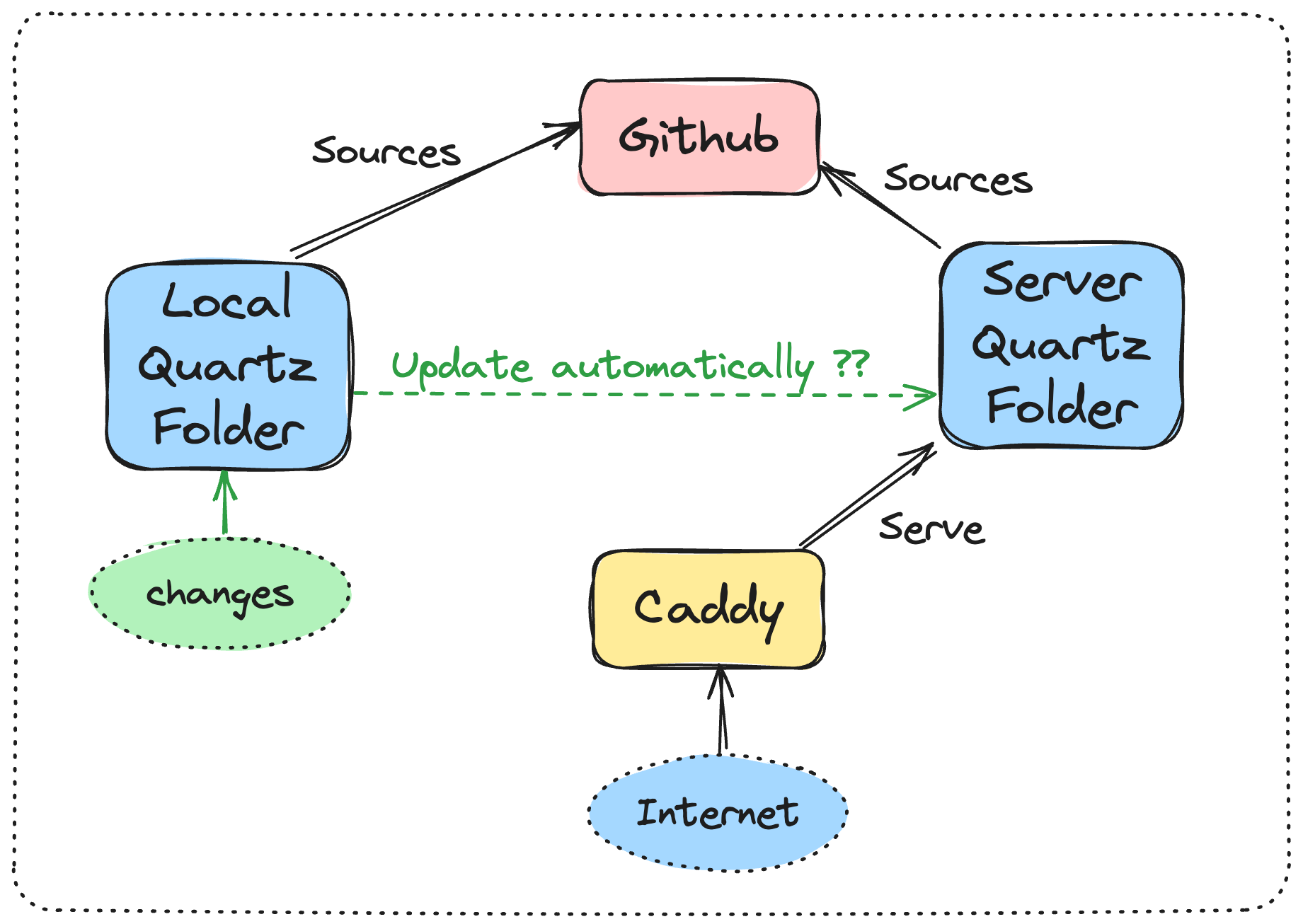
One straightforward approach is to update the Git repository directly, which is served by Caddy, using the git pull command, followed by rebuilding the static files. However, this method requires continuous access to the server and involves a relatively manual process.
In this guide, I will demonstrate how to update your server repository by leveraging a combination of Github Webhooks and Caddy configuration.
Create Update Script
Create a shell script named update-quartz with the following content:
#!/bin/sh
# /path/to/script/update-quartz
(cd /path/to/quartz && git pull origin main && npx quartz build)This script will update the git repository then rebuild the Quartz static files from your notes.
Update Caddy Docker Image
Caddy Exec Plugin
caddy-exec is a Caddy plugin designed for executing background shell commands. Its utility becomes evident when employing it to directly run our earlier update script within the Caddy environment.
To add the plugin to your Caddy docker instance, you can use the Dockerfile from 04-install-caddy-plugins:
FROM caddy:builder AS builder
RUN xcaddy build \
--with github.com/abiosoft/caddy-exec
FROM caddy:latest
COPY --from=builder /usr/bin/caddy /usr/bin/caddyScript Dependencies
The update-quartz also have dependencies that needs to be installed:
FROM caddy:builder AS builder
RUN xcaddy build \
--with github.com/abiosoft/caddy-exec
FROM caddy:latest
COPY --from=builder /usr/bin/caddy /usr/bin/caddy
RUN apk add --update nodejs npm gitEnvironment
To be able to execute the update-quartz command, Caddy need the script to be in the PATH variable. Edit the Dockerfile as follow:
FROM caddy:builder AS builder
RUN xcaddy build \
--with github.com/abiosoft/caddy-exec
FROM caddy:latest
COPY --from=builder /usr/bin/caddy /usr/bin/caddy
RUN apk add --update nodejs npm git
ENV PATH="${PATH}:/path/to/script"And add a volume mapping the update-quartz script on the docker-cpopose.yml of Caddy:
version: "3.9"
services:
caddy:
image: caddy:latest
container_name: caddy
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "80:80"
- "443:443"
- "443:443/udp"
volumes:
- ./Caddyfile:/etc/caddy/Caddyfile
- ./data:/data
- ./config:/config
- /path/to/script:/path/to/script
networks:
default:
external:
name: caddyCreate Caddy /update Endpoint
Next, let’s establish an /update endpoint, which will serve as the trigger point for initiating the update of the server’s Git repository through Caddy.
From the Caddy config of 06-caddy-for-quartz, add the configuration below:
domain.name {
route /update {
exec update-quartz
}
root * /path/to/quartz/public
try_files {path} {path.html}
file_server
handle_errors {
@404-410 expression `{err.status_code} in [404, 410]`
handle @404-410 {
root * /path/to/quartz/public
rewrite * {err.status_code}.html
file_server
}
}
}With this configuration, the update can be triggered manually by calling the /update endpoint on our server.
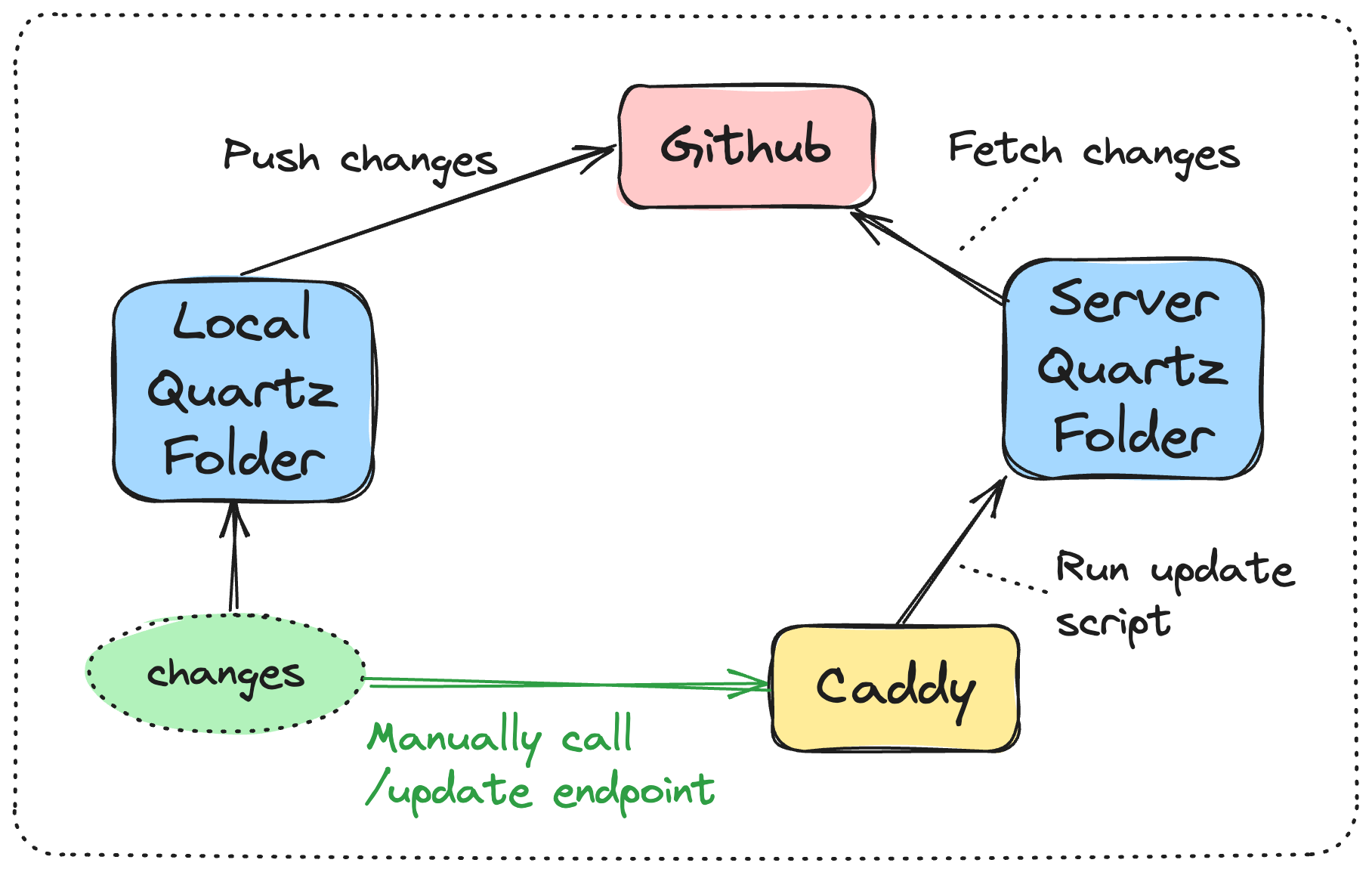
This endpoint is currently accessible by all the internet. To create a basicauth authentication protection, generate a password hash using the command:
docker exec -it caddy caddy hash-passwordFor the password 1234, the output will look like:
Enter password:
Confirm password:
$2a$14$S9xXKUJUueIzZFFPFhrqQOkCJs.12XeyHSybjpXNBLCLQWli7wIvaThis command will output a string in the bcrypt format by default. You can look at the Caddy hash-password documentation for more information.
Complete the Caddy config file with basicauth directive, specifying the hash-password output and a user that will be used to authenticate:
domain.name {
route /update {
basicauth {
user $2a$14$S57sqa8RAHPBTRYvy.GqYOQOoPBeip.zZ9W.yvmQKck61thG72bKy
}
exec update-quartz
}
root * /path/to/quartz/public
try_files {path} {path.html}
file_server
handle_errors {
@404-410 expression `{err.status_code} in [404, 410]`
handle @404-410 {
root * /path/to/quartz/public
rewrite * {err.status_code}.html
file_server
}
}
}With this configuration, the endpoint /update will be protected with credentials user/1234.
Setup Github Webhook
Go to Github in Settings => Webhooks => Add webhook.
For the Payload URL parameter, set the URL https://user:1234@domain.name/update.
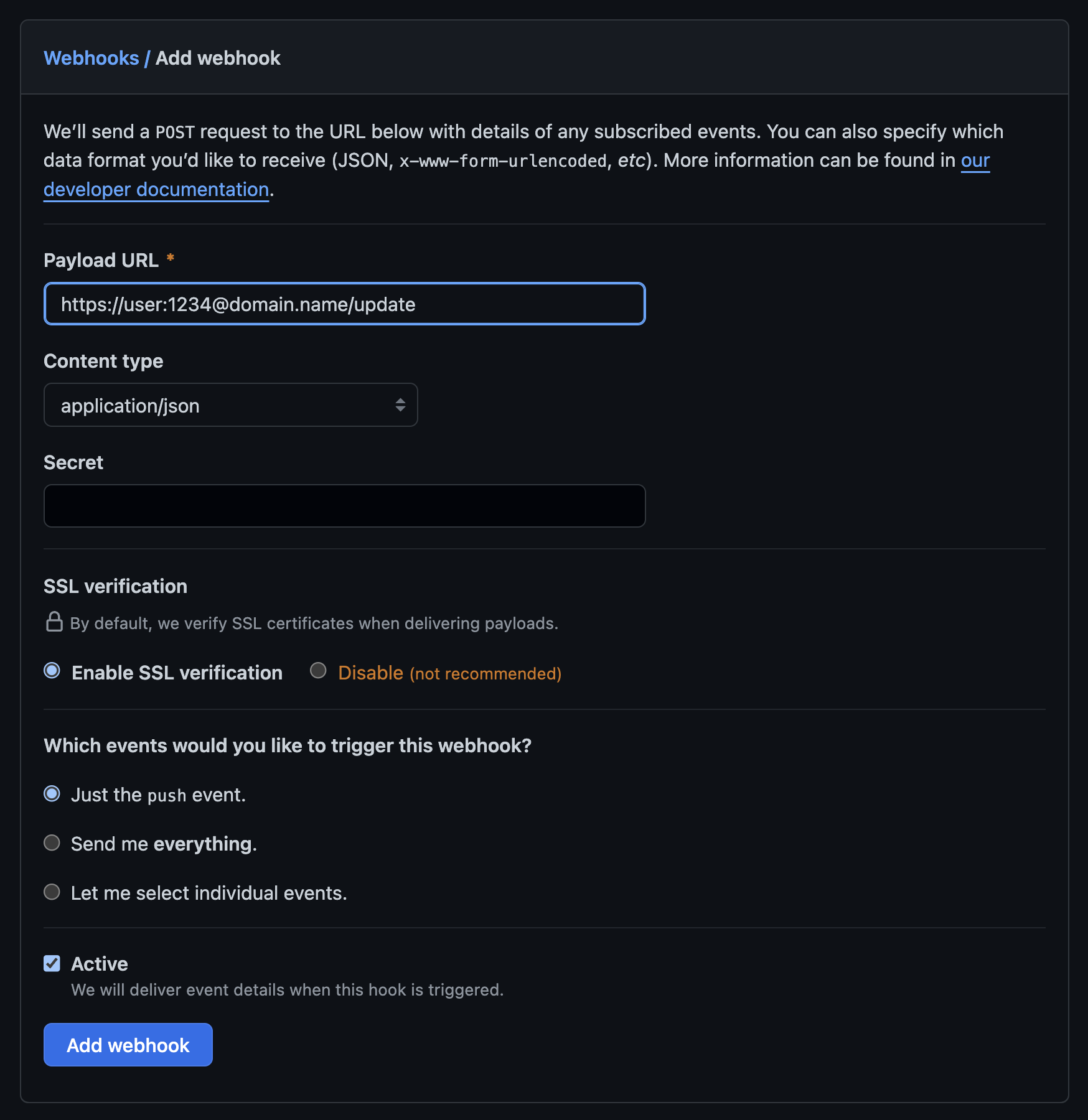
By default, webhooks will be triggered on push event. This implies that when you push your modifications to Quartz on Github, the webhook will autonomously activate the /update endpoint on your Caddy server. Consequently, it will update and rebuild the Quartz static files, which are also served by your Caddy instance 🚀.

Improve Security
To safeguard your Caddy endpoint /update from potential brute force attacks, consider implementing custom Fail2Ban filters as outlined in the blog post 05-fail2ban-for-caddy.
Ressources
- Caddy Plugin caddy-exec
- Caddy Documentation
- basicauth directive
- route directive
- hash-password command
- Github Webhooks